Debt Mutual Funds
Bajaj Finserv Banking and PSU Fund
Debt Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv Money Market Fund
Debt Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv Overnight Fund
Debt Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv Liquid Fund
Debt Fund Regular GrowthWhat are debt mutual funds?
Debt funds are mutual funds that invest primarily in fixed-income securities such as government bonds, corporate bonds, treasury bills and commercial papers. They typically offer modest returns and entail low/low-to-moderate risk. They can be suitable for conservative investors, those with short-term goals, and those looking to diversify their portfolio across debt and equity to balance risk and return potential.
How do debt funds work?
A debt or fixed-income security represents a loan given by one party to another. In the case of debt mutual funds, the loan is given by an investor to a government or a corporation. The borrower agrees to repay the principal amount at maturity and make interest payments at specified intervals. The return potential of debt securities comes from these interest payments. Bonds, debentures, and treasury bills are common types of debt securities.
Debt mutual funds invest in a diverse portfolio of such securities. They may invest in short-term, medium-term, long-term fixed-income instruments or a combination of these, depending on the scheme category and investment objective.
Who should invest in debt funds?
Here are some types of investors who may consider investing in debt mutual funds:
- Conservative investors: Investors with a low or moderate risk appetite may find debt funds suitable as they offer modest return potential with relative stability of capital invested.
- Those seeking a steady income stream: If the borrower pays the interest on schedule and as planned, debt mutual funds can result in a potentially steady income stream. However, it is important to ensure that the mutual fund invests in high-quality securities or government securities with minimal default risk.
- Those who want to build an emergency corpus: Most debt funds are also usually liquid, so they can be a good avenue for an emergency corpus. The relative stability of capital also makes debt fund investments suitable for parking cash for contingencies. Debt funds with a low portfolio duration, such as overnight funds, liquid funds or money market funds, are suitable for such a corpus.
- Short-term investors: The relative stability of debt funds can make them more suitable than equity for short-term investments. Equity funds have a higher return potential but are recommended for longer horizons as there can be significant fluctuations in the value of the investment in the short term.
- Those parking surplus cash:Investors who want to temporarily park surplus funds in an avenue that has better return potential than bank accounts may consider short-term debt funds such as overnight funds or liquid funds.
- Investors seeking to diversify: Portfolio diversification is important for mitigating risks. Equity mutual fund investors can seek to diversify a part of their portfolio into debt funds to lend relative stability to their investments.
- Investors nearing their goals: Equity investors who are nearing retirement or other goals can contemplate gradually transitioning to lower-risk avenues such as debt mutual funds to mitigate the impact of volatility on their investments.
How to invest in debt funds online?
To invest in a Bajaj Finserv AMC debt mutual fund, follow these steps:
- Browse the website and select a scheme
- Click on ‘Invest Now’ from the scheme page or the website home page. You will be redirected to the investor portal.
- Log in if you are an existing investor, or else sign up. To sign up, you will need to enter some basic information such as your name, date of birth, PAN details and bank account information. You may also be asked to complete your Know Your Customer (KYC) verification process if you are not KYC validated.
- From the dropdown menu, select the scheme you wish to invest in and the mode of investment (lumpsum or SIP). Enter the investment amount and select the payment method. You can also invest online as well as offline through your distributor or through aggregator platforms.
Types of debt funds
There are several debt mutual fund categories in India, each investing in securities with different maturity lengths. These include:- Overnight funds: Invest in overnight securities with a maturity of one day.
- Liquid funds: Invest in debt and money market securities with maturities of up to 91 days.
- Money market funds: Invest in money market instruments such as treasury bills, commercial papers and certificates of deposits with maturity of up to one year.
- Ultra short duration funds: Invest in debt and money market instruments; portfolio has a Macaulay duration of three to six months.
- Short duration funds: Invest in debt and money market securities, maintaining a portfolio Macaulay duration of one to three years.
- Medium duration funds: Invest in debt and money market securities and has a portfolio Macaulay duration of three to four years.
- Long duration funds: Invest in debt and money market securities and maintains a portfolio Macaulay duration of more than seven years.
- Dynamic bond funds: Invests in debt securities across durations, adjusting the portfolio based on interest rate movements.
- Credit risk funds: Invest in lower-rated corporate bonds (AA and below), aiming for higher returns with increased credit risk.
- Corporate bond funds: Focus on high-rated corporate bonds (AA+ and above).
- Gilt funds: Invest in government securities with varying maturities.
- Fixed maturity plans: Closed-end funds investing in fixed-income securities maturing on a specific date.
- Banking and PSU funds: Invest in debt securities issued by banks and public sector undertakings, aiming for stability and moderate returns.
Before choosing a debt fund investment, investors should consider the credit quality of the underlying bonds within the fund's portfolio. Higher-rated bonds typically offer lower yields but come with lower credit risk, while lower-rated bonds may provide higher yields but carry increased credit risk.
Additionally, investors should evaluate the fund's average maturity and duration, as these factors influence sensitivity to interest rate fluctuations. The rate of a fixed income security is inversely proportional to the prevailing interest rates in the economy. So as interest rates rise, bond prices fall, and vice versa. A higher duration typically indicates higher return potential but also greater sensitivity to interest rates, implying higher risk.
How are debt funds taxed?
Any gains made on debt fund investments are considered short-term capital gains, irrespective of the holding period. They are added to your annual income and taxed at the applicable income tax slab rate.
Advantages of debt mutual funds
Debt mutual funds are a popular avenue for those seeking relatively stable investments with reasonable return potential. Here are some key advantages:
- Offer potential for relatively steady returns with lower risk compared to equity funds
- Provide high liquidity, making it easy to access funds
- Are generally less sensitive to market volatility
- Suitable for short or medium term goals where relative stability of invested capital is important
- Offer a range of options, from liquid funds to corporate bonds, catering to various risk profiles
- Can act as a hedge in a diversified portfolio, balancing out high-risk assets
Things to consider before investing in debt mutual funds
Here are a few things to keep in mind when making debt fund investments:
- Return potential: The return potential of debt securities is typically less than that of equity. If you have a long investment horizon, a high risk appetite and are seeking long-term wealth-building potential, you may find equity funds more suitable.
- Risk profile: Debt funds carry varying levels of risk based on factors such as credit quality, interest rate sensitivity and liquidity. Choose funds that match your risk appetite. Interest rate risk can be mitigated by investing in debt funds with a low portfolio duration. Credit risk can be mitigated by investing in high-quality papers issued by the government or corporates rated AAA and above.
- Time horizon: Consider your investment timeline. Debt mutual funds with a low portfolio duration such as money market funds, ultra-short duration funds and short duration funds may be more suitable for short-term goals, whereas long-duration funds, dynamic bond funds, banking and PSU funds and gilt funds may be more suitable for longer investment horizons.
Learn About Mutual Funds

Investing isn’t just about numbers,…

In today’s fast-paced consumerist…

When markets fluctuate significantly…

Gold has traditionally been used in…

Image for representation purposes…

Gold often draws attention when…

Of the almost 4 crore unique…

Traditional wisdom in the mutual…

Retail investors predominantly…

A common question among investors is…
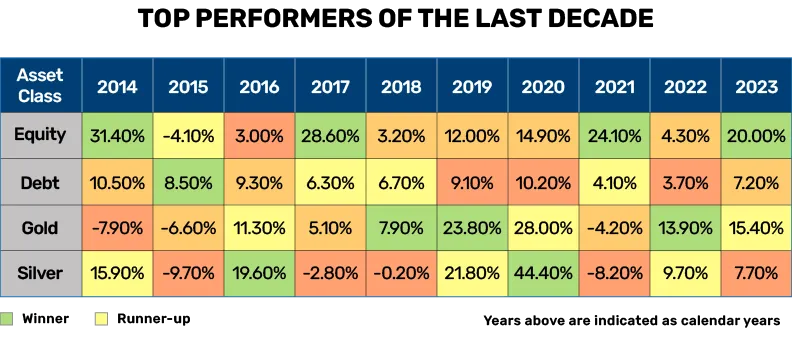
Equity, debt, gold, and silver have…

Recently, at a bustling farmers’…

Walk into your closet and take a…

You may not realise it, but when you…

Over the years, mutual funds have…

Planning for retirement involves…

Securing a comfortable post-…
Frequently Asked Questions
A debt fund is a type of mutual fund that primarily invests in fixed-income securities such as government or corporate bonds. These funds generate returns through interest income and are typically less volatile than equities.
There are no risk-free debt funds. Despite their relative stability, debt funds do not guarantee returns or capital safety. Returns can fluctuate based on market conditions and capital protection is also not guaranteed.
No scheme is inherently better than the other. The type of mutual fund that is suitable for you will depend on your investment goals, risk appetite and investment horizon, apart from other factors. Generally, debt funds may be suitable for investors with a low or moderate risk appetite and a short or medium-term investment horizon.
No, unlike fixed deposits, debt mutual funds do not offer fixed or guaranteed returns. However, they typically offer higher liquidity and flexibility with regard to redemption and additional investments.
The debt fund category that is suitable for you will depend on your investment horizon, risk tolerance, and investment goals. Debt funds that invest in short-term securities may be more suited to short-term goals or investors who want reduced interest rate risk. Medium- or long-duration funds can offer higher return potential over a slightly longer horizon, but with greater interest rate risk. Assess factors such as the credit quality and duration of the underlying assets when choosing a debt fund investment option. You can also diversify across different types of debt securities to balance risk and return potential.
Investing in Bajaj Finserv Liquid Fund can help you obtain relatively better returns as compared to a traditional savings account. Also, since liquid funds invest predominantly in highly rated money market instruments, they are a relatively stable investment option. Lastly, you can redeem your units of Bajaj Finserv Liquid Fund at any time with T+1 settlement timeline and plan your liabilities.
Individuals, corporates including SMEs, partnership firms, NRIs, charitable trusts, etc., can invest in Bajaj Finserv Liquid Fund.
Mutual Fund Videos: Watch, Learn, Invest

Presenting 'The Third Source', our…
Presenting 'The Third Source', our…
Presenting 'The Third Source', our…

